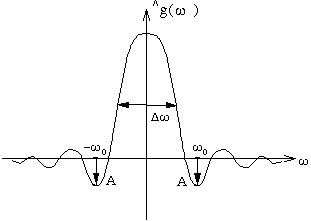
The properties of the windowed Fourier transform are determined by the window g, or rather its Fourier transform, whose energy should be concentrated around 0. Three important parameters evaluate this energy spread:

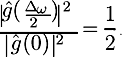
If Dw is small, the energy of the window is well concentrated around 0.
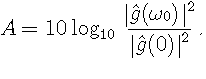
These side lobes can create "shadows" on each side of the frequency center.
It sums up the behavior of the Fourier transform beyond the first side lobes.
The following table gives the values of these parameters for classical windows, normalized so that g(0) = 1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|